Consuming any psychoactive substance—legal or illegal—carries certain risks. Practicing harm reduction techniques and reading up on substances you plan to use will greatly minimize these risks and could possibly save your life. It's good practice when using recreational drugs to use as many of these techniques as possible.
Reagent Testing
Reagent testing is the process of using various testing kits to identify substances. In the world of recreational drugs using reagent tests helps greatly increase the chances that you know what you're putting into your body. It should be noted that reagent testing does not provide a 100% guarantee that you know what you have, but using testing kits is still much safer than ingesting an untested product.
What can be tested for?
Most recreational substances and certain common alduterants can be tested for depending on what testing kit is used. For a full list of testable substances and their reactions please take the time to check out the testing kit sections of DanceSafe and Bunk Police. In an ideal scenario it is recommended that all four of the most common tests are used (Marquis, Mecke, Madelin, Simon's) but if you can only afford to get one the Mecke Reagent is recommended.
Testing kits can be purchased from our partners over at DanceSafe and Bunk Police. If you choose to buy them from another source take the time to research the reputation of the vendor.
What are the steps in reagent testing?
- Scrape a tiny bit of your pill or powder onto a large, white ceramic plate. Use just enough powder to see on the plate.
- Take the reagent bottle out of the plastic safety container. Remove the cap and turn the bottle upside-down a couple inches over the powder. Squeeze one drop out of the bottle onto the powder. Be careful to not let the dropper bottle touch your powder or you will contaminate and ruin the rest of the reagent. Replace the cap.
- Observe the color change right away. Refer to the chart that should have come with your testing kit to determine the substance(s).
Never have more than one reagent bottle open at a time. If you mix up the caps and put the wrong cap on the wrong reagent bottle, this may cross-contaminate the reagents and ruin them. Be sure to perform the tests in a well-lit location. Be careful when using the reagents, as they contain chemicals that can damage skin (we recommend wearing latex gloves). Keep the solutions far from your eyes and mouth. Also, make sure to clean up completely after each test.
Common Festival Drugs
Below is a list of the most popular psychoactive substances at music festivals. Hover overTouch each image to read a basic overview including other names (street names and slang terms), the effects classification, common adulterants, and commonly encountered substitutes. Common substitutes refers to other substances that are often falsely advertised as the being the original substance. For example, a dealer passing off Methylone as MDMA.
For a more information on these and many more substances including dose information, health concerns and user experiences, please visit our partners at Erowid.

MDMA
MDMA
MDMA is an empathogenic stimulant known for its euphoric effects on users.
Other Names: Ecstasy, Molly, E, X, XTC
Classification: Empathogen, Stimulant
Common Adulterants: Caffeine, DXM, Methamphetamine, Methylone
Common Substitutes: Methylone

LSD
LSD
LSD is the best known and most researched psychedelic. It is the standard against which all other psychedelics are compared.
Other Names: Acid, L, Lucy, Tabs
Classification: Psychedelic
Common Adulterants: None*
Common Substitutes: 25x-NBOMe series, DOx series

Ketamine
Ketamine
Ketamine is a dissociative anesthetic with psychedelic effects ranging from mild to strong depending on the dose.
Other Names: K, Special K, Kittens
Classification: Dissociative
Common Adulterants: None*
Common Substitutes: Methoxetamine (MXE), Tiletamine

Cannabis
Cannabis
Cannabis, a fast-growing bushy annual with dense sticky flowers, produces the psychoactive THC. It is the most widely used illegal psychoactive.
Other Names: Weed, Pot, Marijuana
Classification: Intoxicant, Depressant, Stimulant, Psychedelic
Common Adulterants: None*
Common Substitutes: None

Alcohol
Alcohol
Alcohol is one of the most common strong psychoactives used by humans. It has a long history of use and its intoxicating effects are well-studied.
Other Names: Liquor, Spirits, Wine, Beer
Classification: Depressant, Intoxicant
Common Adulterants: Not Applicable
Common Substitutes: Not Applicable

Cocaine
Cocaine
Cocaine is a common stimulant derived from the Erythroxylum coca plant. It is best known for its massive popularity in powdered and freebase (crack) forms.
Other Names: Coke, Crack, Blow, Yayo
Classification: Stimulant
Common Adulterants: Caffeine, Ephedrine, Inositol, Sucrose, Talc, Lactose
Common Substitutes: None

Mushrooms
Mushrooms
There are more than 180 species of mushrooms which contain the psychoactive compounds psilocybin and psilocin.
Other Names: Shrooms, Magic Mushrooms
Classification: Psychedelic
Common Adulterants: None*
Common Substitutes: 4-AcO-DMT and similar tryptamines (sold as "mushroom powder" or "psilocybin extract")

DMT
DMT
DMT is a powerful, visual psychedelic which produces short-acting effects when smoked. It is used orally in combination with an MAOI, as in ayahuasca brews.
Other Names: Deems, Dmitri
Classification: Psychedelic
Common Adulterants: None*
Common Substitutes: 5-MeO-DMT

Mescaline
Mescaline
Mescaline is a naturally occurring psychedelic with a long history of human use. It is found in a several species of cacti, most notably Lophophora williamsii (Peyote).
Other Names: Mescalito
Classification: Psychedelic
Common Adulterants: None*
Common Substitutes: None

MDA
MDA
MDA is a synthetic empathogen sometimes found in ecstasy tablets. It is closely related to MDMA though its effects are said to be slightly more psychedelic.
Other Names: Sass
Classification: Empathogen, Psychedelic
Common Adulterants: Caffeine, DXM, Methamphetamine, Methylone
Common Substitutes: Methylone, 6-APB
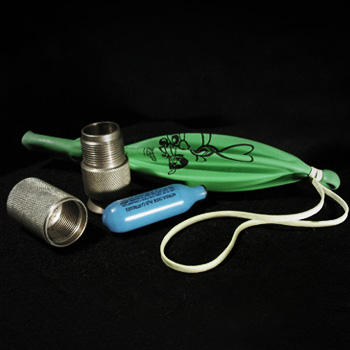
Nitrous Oxide
Nitrous Oxide
Nitrous Oxide is an anaesthetic gas best known for its use in dentistry and as a whipped cream propellant. It is widely available and its effects are short lasting.
Other Names: Hippy Crack, Whippets, Laughing Gas, N20, Nangs
Classification: Dissociative
Common Adulterants: Not Applicable
Common Substitutes: None

GHB
GHB
GHB is a sedative used both as a prescription sleep-aid and as a recreational intoxicant. It is known for its ability to induce a short (several hour) coma-like sleep at high doses.
Other Names: G, Sodium Oxybate, Xyrem
Classification: Depressant, Intoxicant
Common Adulterants: None*
Common Substitutes: GBL
*A substance having no common adulterants does not mean cuts are never used, just that it is uncommon compared to other substances. Caution should still be used with these substances.